With 2023 dubbed the year of Generative AI, what advancements, trends, and use cases might we expect in 2024 and beyond?
To find out we need to look at recent research and AI stats.
In this article, we’re analyzing the statistics and trends informing the adoption and use of AI.

Throughout, we’ll comment on what those AI statistics mean as well as add insights from some of the developers on the HatchWork’s team who are part of our Generative-Driven Development—a method that has led to a 30-50% productivity increase for our clients.
What you’ll be left with is a clear overview of the state of Generative AI and its future.
- The Current State of the Global AI Market
- What Tools Are We Using? Core AI Technologies and Generative AI Systems
- Developer Insights on Generative AI: How is it Impacting Software Development
- Key Statistics and Trends in Generative AI
- The Impact of Generative AI on Employment and Skill Development
- Ethical Considerations and Regulatory Landscape
- Looking Forward: Where Is Generative AI Going Next?
The Current State of the Global AI Market
🗝️Key takeaway: AI is a growing industry, with projections showing an annual growth rate of 37.3% between now and 2030. It’s largely fueled by advancements and the adoption of Generative AI.
AI tech and its potential has mesmerized the world for decades.
Film and TV have long projected a world where artificial intelligence is a facet of everyday life—to both sinister ends (iRobot) and peaceful coexistence (the Jetsons).
We’re closer than ever to finding out just how well humans and artificial intelligence can live side by side. And as a whole, we’re investing big in its development.
In 2022, Precedence Research found the global artificial intelligence market was valued at USD 454.12 billion. It showed North America having the biggest piece of the pie, with their AI market valuation hitting USD 167.30 billion.
In the image below you can see how much money is being invested into AI by geographic area.

And the AI market is only set to grow. In fact, McKinsey projects an economic impact of $6.1-7.9T annually.
Behind much of this growth, high valuation, and investment is the development and increased use of Generative AI.
Gartner reports that in the last 10 months, half of the 1,400+ organizations they surveyed have increased investment in Generative AI.
They’ve also found that 44% of organizations are piloting generative AI and 10% have put it into production. Compare that to 15% and 4% respectively in just March and April of 2023.
The rapid adoption of generative AI demonstrates its potential to revolutionize how we work, the skills we need, and the type of work we will do.
What’s driving our need for AI? It’s a mix of:
- Increased Demand in Various Sectors: AI solutions are increasingly sought after in healthcare, finance, and retail. Check out our guide on use cases across various industries.
- Advancements in Generative AI: Innovations in neural networks are propelling AI capabilities forward.
- Big Data Availability: The rise in big data availability aids in training more sophisticated AI systems.
- Complex Data Analysis: AI’s ability to analyze complex datasets is invaluable in numerous applications.
- Digital Transformation and Remote Work: The shift towards remote work and digital operations has accelerated the adoption of AI technologies in business.
What Tools Are We Using? Core AI Technologies and Generative AI Systems
🗝️ Key takeaway: With systems like ChatGPT, AlphaCode, and DALL-E 2 leveraging vast datasets, industries are witnessing a shift towards more intuitive, creative, and efficient processes.
Generative AI relies on core technologies like deep learning and neural networks.
These technologies empower AI systems to learn from vast datasets and generate new, original content. This capability extends across domains, from language processing to visual art creation, and code development. It’s changing how tasks are approached and executed on a daily basis.
Generative AI : A Brief Definition 📖
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that can create new content or data, which they were not explicitly programmed to produce.
These systems use advanced machine learning techniques, such as deep learning, neural networks, and transformer technology to analyze and learn from large datasets, and then generate original outputs.
This can include tasks like writing text, composing music, creating images or videos, and even generating new ideas or solutions.
Among the most notable tools leveraging generative AI is OpenAI’s ChatGPT, known for its ability to engage in human-like conversations and provide informative responses. It exemplifies the advanced natural language processing capabilities of these systems.
Here’s a list and description of other core Generative AI tools people across industries are adopting:
- AlphaCode: An advanced tool designed for programming challenges, utilizing AI to write and optimize code.
- Mid Journey: Specializes in generating detailed and imaginative visual narratives based on text prompts.
- Copilot: Developed by GitHub, this AI system transforms natural language prompts into coding suggestions in various programming languages. It’s complemented by similar systems like OpenAI’s Codex and Salesforce’s CodeGen.
- Katalon: A comprehensive tool for automated testing, integrating AI to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of software testing processes.
- Amazon Bedrock: A robust AI platform by Amazon, designed to provide deep insights and analytics, supporting various AI applications and data processing tasks.
- CodeGPT: A specialized AI tool for coding assistance, offering features like code completion and debugging suggestions based on Generative AI models.
- Hugging Face: Known for its vast repository of pre-trained models, Hugging Face is a platform that facilitates AI development, especially in natural language processing.
- Llama by Meta: An AI system developed by Meta, aimed at pushing the boundaries in various aspects of AI, including language understanding and generative tasks.
- Make-A-Video: A revolutionary system that enables the creation of videos from concise text descriptions, opening new possibilities in media production.
- AI Query: A tool designed for streamlining data analysis and simplifying complex data interactions using AI.
- Bard: Focuses on content generation, leveraging AI to assist in writing and creative tasks.
- DALL-E 2: OpenAI’s image generation AI, known for creating detailed and artistic images from textual descriptions.
- Copy.ai: Aims at automating content creation, particularly in marketing and advertising, using AI to generate high-quality written content.
- Murf.ai: Specializes in voice synthesis, enabling the creation of realistic and customizable AI-generated voices for various applications.
This list is truly the tip of the iceberg. Every day new tools are launched into the AI ecosystem.
Time will tell which of them become indispensable to the modern work landscape or who may fall into the deep abyss of almost forgotten memory—anyone remember Ask Jeeves? Or AIM? We do…just barely.
Developer Insights on Generative AI: How is it Impacting Software Development
🗝️ Key takeaway: Generative AI is already a fixture in the work processes of forward-thinking software developers with data on productivity proving its a worthwhile addition to the industry.
A recent McKinsey report claims Software Engineering will be one of the functions most impacted by AI.
The data and lived experiences of developers back that claim up.
ThoughtWorks reports software developers can experience 10-30% productivity gains when using Generative AI.
While GitHub has run its own studies on the use of CoPilot by software developers and seen positive results on productivity and speed of task completion.
Across two studies (1 and 2) they’ve found developers who use Copilot are:
- 55% faster in general
- 88% more productive
- 96% faster with repetitive tasks
- 85% more confident in code quality
- 15% faster at code reviews
At HatchWorks, our integration of AI has revolutionized our Generative-Driven Development™ process, resulting in a 30-50% productivity boost for our clients.
By utilizing these tools, our engineers have streamlined coding and minimized errors, fundamentally transforming our project delivery methods.
These advancements highlight the significant role of AI in enhancing efficiency and spurring innovation in our field.
To delve deeper into this transformative journey, HatchWorks’ engineers have shared with us their perception of Generative AI tools and how they’re using them to enhance their work.
Jerrik Arango on how he uses ChatGPT: "Combining Copilot with ChatGPT, I’ve found ways to speed-up problem solving and improve code quality. It’s like having a digital peer to consult with, saving time and enhancing my coding practice."
Jerrik Arango
Principal Software Engineer, HatchWorks
Fernando Manzo on the need for developers to use AI to keep up: "If you don’t use AI today, you won’t deliver at the same capacity as your peers. Customer and manager expectations are changing as a consequence of this."
Fernando Manzo
Full Stack Engineer, HatchWorks
Gabriel Bejarano on how human developers are still far too essential to building software: "AI will not replace developers, at least not in the near future. There's lots of creativity involved in the process."
Gabriel Bejarano
Full Stack Engineer, HatchWorks
Key Statistics and Trends in Generative AI
🗝️ Key takeaway: The world is divided in its trust of AI but businesses are using it to fill shortages and increase productivity in the workplace.
We’ve covered the state of AI, highlighted some core tools and technologies, and talked specifically about how Generative AI is impacting Software Development.
Now we’re covering other key artificial intelligence statistics and trends that are defining the opinions, use, and impact of Generative AI.
Trend: Programming/Software Development is Seeing the Most Impact on Productivity
Stat: AI improves employee productivity by up to 66%.
Across 3 case studies by the Nielsen Norman Group:
- Support agents who used AI could handle 13.8% more customer inquiries per hour.
- Business professionals who used AI could write 59% more business documents per hour.
- Programmers who used AI could code 126% more projects per week.
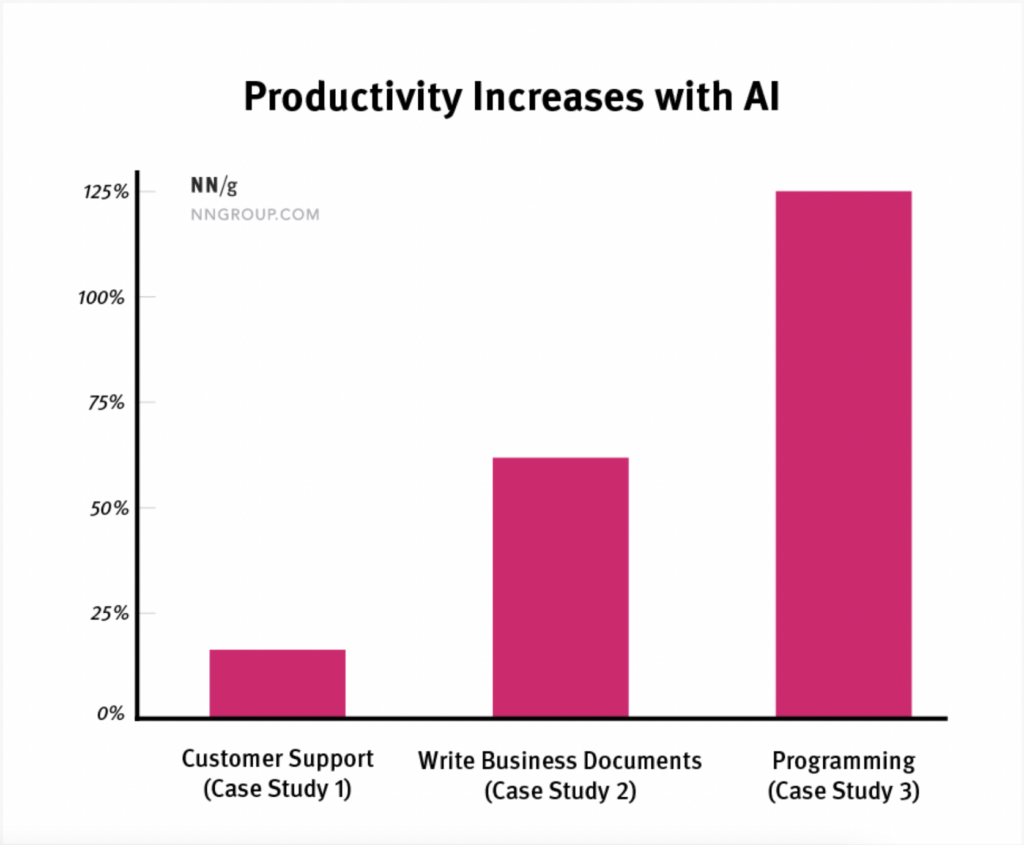
What it means: It’s not just one industry or function that stands to benefit from AI. It’s all of them.
AI tools likely assist in faster query resolution, provide automated responses for common questions, and offer real-time assistance to agents, thus reducing response times and increasing the number of inquiries handled.
They also can assist in tasks like data analysis, content generation, and automated formatting, enabling professionals to produce higher volumes of quality documents in less time.
In the case of programming, this leap in productivity could be attributed to AI’s ability to automate routine coding tasks, suggest code improvements, and provide debugging assistance, allowing programmers to focus on more complex and creative aspects of coding.
Trend: Adoption of Generative AI is Explosive
Stat: ChatGPT reached 100 million monthly active users within 2 months of launch, making it the fastest-growing consumer application in history.
What it means: Word of mouth marketing and an impressive display of the capabilities of Generative AI likely fueled such fast and widespread adoption.
It suggests we’re hungry for tools that optimize our work while reducing time and money spent elsewhere. It wasn’t a case of if we’d be adopting AI but rather a case of when and for what.
"ChatGPT is my go-to tool for deciphering complex and overly architected legacy code, helping me bring clarity and structure to challenging projects."
Wilver Melendez
Full Stack Engineer, HatchWorks
Even Bill Gates has been impressed by the capabilities of Generative AI. He recently wrote a piece titled, The Age of AI has begun. In it he claims to have seen only two truly revolutionary advancements in his lifetime; one being the graphical user interface, the second being ChatGPT.
He even wrote upon witnessing the capabilities of ChatGPT, ‘I knew I had just seen the most important advance in technology since the graphical user interface.’
So not only is the adoption of generative AI explosive in its numbers, it’s explosive in what it can do.
Trend: The East is Generally More Accepting of AI as a Benefit
Stat: In a 2022 IPSOS survey, 78% of Chinese respondents agreed with the statement that products and services using AI have more benefits than drawbacks.
Those from Saudi Arabia (76%) and India (71%) also felt the most positive about AI products. Only 35% of surveyed Americans agreed that products and services using AI had more benefits than drawbacks
What it means: Notably, the US exhibits more skepticism towards Generative AI than other leading nations.
Earlier there was a stat showing Americans are privately investing the most in AI, followed by China. It’s interesting to see the countries that most trust and least trust AI are the ones investing the most heavily in it.
What comes of this could be reminiscent of the US’s space race with the former USSR. The biggest difference is that Generative AI is accessible to the world’s population in a way space technology never was (or likely will be).
And it prompts questions about whether AI technology is more or less dangerous in the hands of everyday people compared to governments. And whether American skepticism of the AI space is rooted in the potential for government overreach, foreign interference, job security, or how autonomous AI thought can become.
Trend: Trust in AI is Divided Among Those with Geographic and Demographic Differences
Stat: Another survey shows that 3 out of 5 people (61%) are wary about trusting AI systems, reporting either ambivalence or an unwillingness to trust. They looked at geographical location as well as generational divides. This time India came on top and Finland bottom.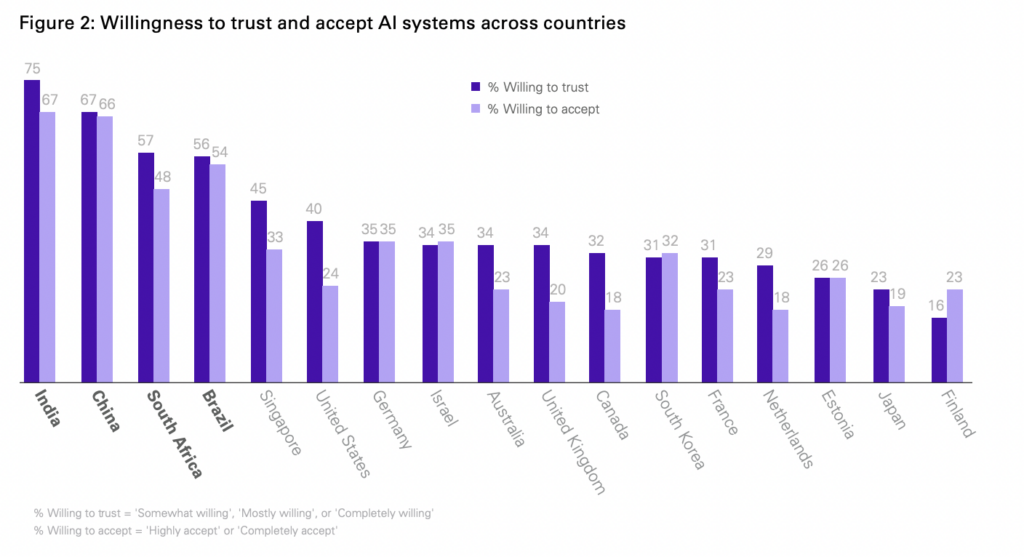
When we break it down by generation and education we see the young are more trusting of AI as are the higher educated. Those in manager roles are also more trusting.
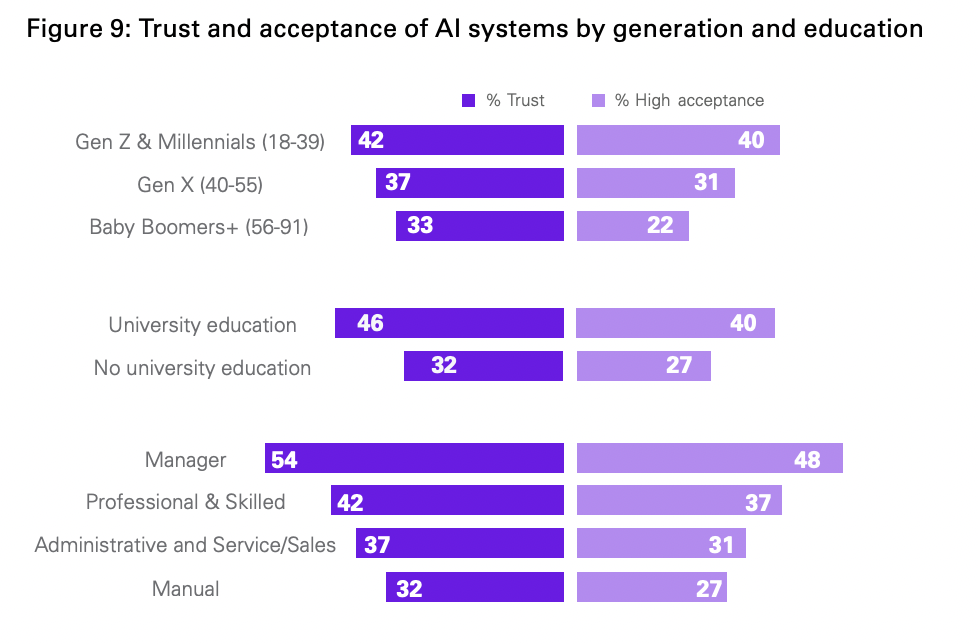
What it means: Younger people are typically more accepting of advancement in technology than their older counterparts. This stat is thus unsurprising. It’s also unsurprising that managers see the value of AI given their job is to make their teams and departments more efficient and productive. AI is a proven way of doing so.
Trend: Generative AI is Being Used to Fix Labor Shortages
Stat: 25% of surveyed companies are turning to AI adoption to address labor shortage issues, according to a 2022 IBM report.
What it means: The fact that companies are turning to AI in response to labor shortages suggests that AI is increasingly seen as capable of filling gaps left by human workers. This could be in areas like data processing, customer service (through chatbots), and even more complex tasks that require learning and adaptation.
To learn more, watch or listen to Episode 11 of the Built Right Podcast, How Generative AI Will Impact the Developer Shortage.
Trend: Businesses Believe in Generative AIs Ability to Boost Productivity
Stat: A significant 64% of businesses believe that artificial intelligence will help increase their overall productivity, as revealed in a Forbes Advisor survey.
What it means: The belief in AI’s role in increasing productivity suggests businesses see AI as a tool for driving growth. This may involve automating routine tasks, optimizing workflows, or providing insights that lead to more informed decision-making.
This statistic also reflects a response to the rapidly changing market demands and the need for businesses to remain competitive. AI adoption can be a key differentiator in responding quickly to market changes and customer needs.
Worryingly, we should watch that human contribution and value aren’t overlooked to the detriment of the company. Sometimes it’s our humanity that is our best differentiator and businesses should be wary of passing on too much, too quickly to our AI sidekicks.
The Impact of Generative AI on Employment and Skill Development
🗝️ Key takeaway: AI isn’t replacing our need for human intelligence, it’s freeing human intelligence up to do other work which puts demand on us to upskill in the use of AI.
The emergence and growth of generative AI are shaping job markets and skill requirements and will have significant implications for employment and workforce development over the coming years.
Job Market Dynamics:
Increase in Gen. AI-Related Job Postings: A notable trend is the increase in Generative AI-related job postings. LinkedIn reports that job postings on the platform mentioning GPT or ChatGPT have increased 21x since November 2022, when OpenAI first released its AI chatbot into the world.
Job Creation vs. Displacement: A McKinsey report forecasts that AI advancements could affect around 15% of the global workforce between 2016 and 2030. This statistic encompasses both job displacement due to automation and the creation of new jobs requiring AI expertise.
Skill Development and Educational Trends:
Evolving Skill Requirements: With AI’s growing integration across industries, the skill requirements for many jobs are evolving. There’s an increasing need for AI literacy and the ability to work alongside AI systems as evidenced by the earlier stat showing a rise in AI related postings.
"At HatchWorks, Generative AI has fundamentally reshaped not just the development landscape, but also job functions and productivity across every business sector. This technology provides an unprecedented level of speed and precision. It’s not solely about enhancing efficiency; it’s about empowering our teams to innovate at a pace and scale that was previously unimaginable."
Brandon Powell
CEO, HatchWorks
Ethical Considerations and Regulatory Landscape
🗝️ Key takeaway: The recent advancements in AI have made us all question its use and regulation. Governments are finding ways to control it while encouraging its use to advance the world.
The use of AI raises a range of ethical considerations, including concerns about its accuracy, the extent of its capabilities, potential misuse for nefarious purposes, and environmental impacts. And with ethical considerations come questions over how we’ll regulate its use.
Let’s look at how public opinion and emerging research highlight the complexities and challenges in this rapidly evolving field.
Incidents and Controversies:
The number of AI-related incidents and controversies has surged, increasing 26x since 2012.
Additionally, the number of accepted submissions to FAccT, a leading AI ethics conference, has more than doubled since 2021 and increased by a factor of 10 since 2018.
Notable incidents in 2022 included a deep fake video of Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy and the use of call-monitoring technology in U.S. prisons. This trend highlights both the expanding use of AI and the awareness of its potential for misuse.
Interestingly, it’s those who use tools like ChatGPT often that lose our sense of skepticism in its accuracy. Ben Evans gave a talk on Generative AI and showed the following slide:
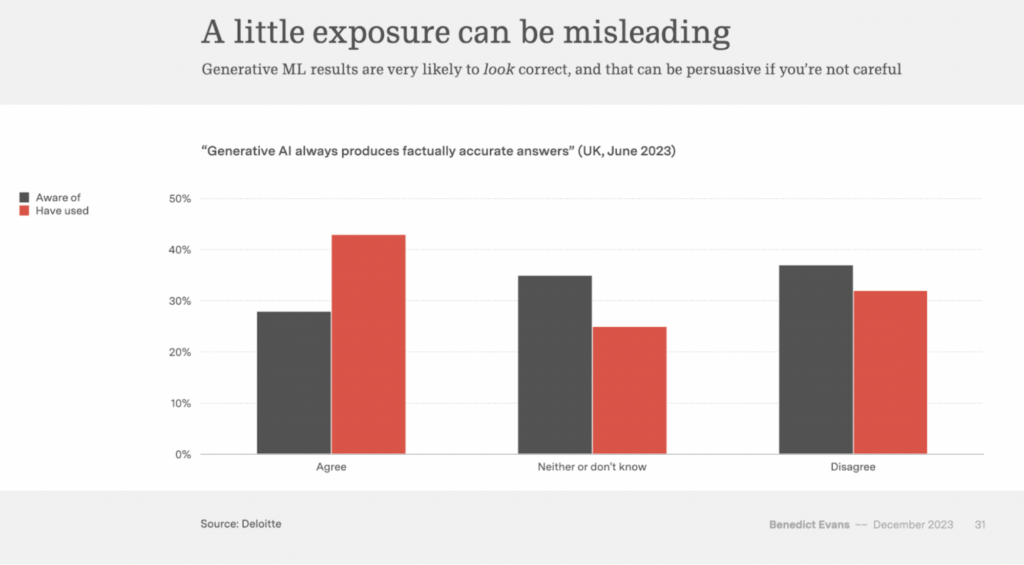
The data from Deloitte shows that use correlates to trust.
Challenges in Reliability and Bias:
Generative AI systems are prone to errors, such as producing incoherent or untrue responses, which raises concerns about their reliability in critical applications.
Issues like gender bias in text-to-image generators and the manipulation of chatbots like ChatGPT for harmful purposes underscore the need for cautious and responsible AI development.
Environmental Impact:
AI’s environmental impact is a growing concern. For instance, the training run of the BLOOM AI model emitted 25 times more carbon than a single air traveler on a one-way trip from New York to San Francisco.
However, AI also offers environmental solutions, such as new reinforcement learning models like BCOOLER, which optimize energy usage.
Public Expectation for Regulation:
A substantial 71% of people expect AI to be regulated.
This sentiment is widespread, with the majority in almost every country, except India, viewing regulation as necessary. This reflects growing concerns about the impact and potential misuse of AI technologies.
In fact, President Biden has already “signed an ambitious executive order on artificial intelligence that seeks to balance the needs of cutting-edge technology companies with national security and consumer rights, creating an early set of guardrails that could be fortified by legislation and global agreements.”
Source: AP News
Looking Forward: Where Is Generative AI Going Next?
Despite the ethical and regulatory considerations outlined earlier, the future of Generative AI appears promising from a growth perspective:
- Goldman Sachs predicts Generative AI will raise global GDP by 7% ($7T).
- McKinsey projects an economic impact of $6.1 – $7.9T annually
- Precedence Research believes the AI Market size will hit around USD 2,575.16 billion by 2032.
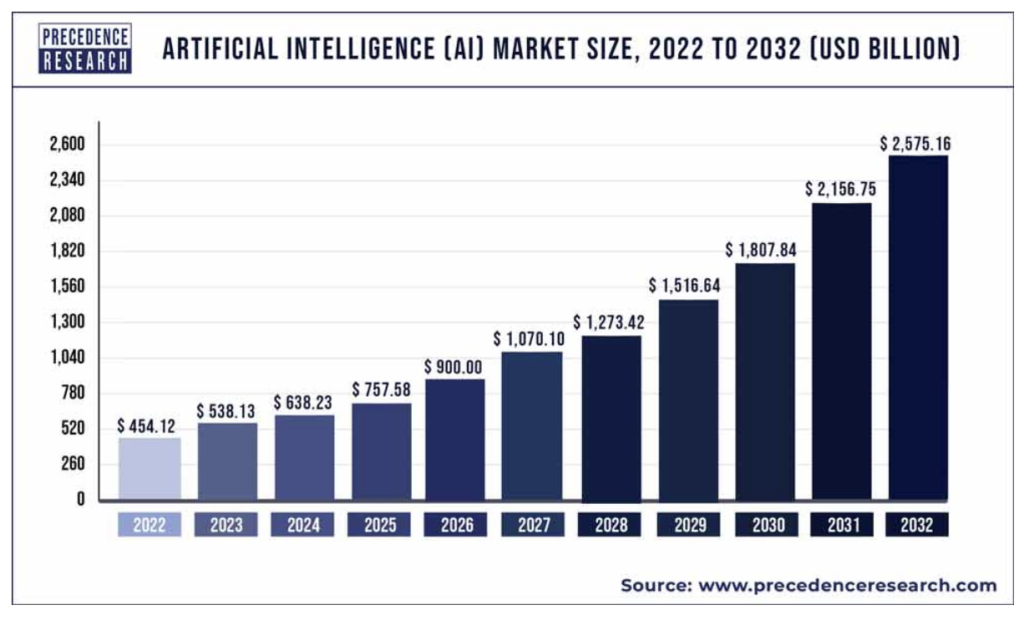
At HatchWorks we’re most focused on the future of AI as it relates to software development.
We expect the use of AI will only advance over time with further improvements to developer productivity, new use cases for how developers use AI to assist software development, and an evolution in the skills and capabilities businesses hire for (internally and through outsourcing).
And we expect that because we’ve already witnessed it firsthand among our own developers:
"ChatGPT guides me in choosing the right design patterns and structures, and helps with creating code examples."
Brian Cornielle Batista
Full Stack Engineer, HatchWorks
"ChatGPT has revolutionized the way I approach project creation. It allows me to concentrate on design and conceptualization, and assists with the more complex aspects of coding."
David Mora Guerrero
Machine Learning Engineer, HatchWorks
Further reading: Generative AI Use Case Trends Across Industries: A Strategic Report
We’ll continue to optimize our approach and inclusion of these AI tools in our processes and equip our Nearshore developers with the education and resources they need to be efficient with them.
If you want to learn more about how our Generative-Driven Development™ services have led to a 30-50% productivity increase for our clients, get in touch here.







