Building with AI in n8n can feel like guesswork if you’re not sure how the pieces fit together. Most tutorials out there give you the parts (like a model, a tool, or a prompt) but not the structure to make them useful.
This guide fixes that. We’ll walk you through how to create AI agents in n8n that are structured, testable, and ready for real-world use. Before you know it, you’ll be sharing your own agent workflow templates and taking your work life to a level of automation you never thought possible.

Keep reading to learn about n8n’s agents, key concepts you’ll need to know, and why the tutorials you’ve read in the past haven’t stuck.
Or jump to the step-by-step tutorial if you want to dive right in.
| Category | Data Governance | Information Governance |
|---|---|---|
|
Scope
|
Data governance focuses on technical data management for structured and unstructured data
|
Encompasses all information assets, including data, documents, records, and communications. Ultimately, overseeing how data is used and protected
|
|
Goals
|
Data governance emphasizes data quality and usability
|
Information governance prioritizes compliance and risk management.
|
|
Stakeholders
|
Involves IT teams, data engineers, and analysts
|
Involves legal teams, compliance officers, executive leadership, and risk management teams
|
|
Policies and Procedures
|
Defines data collection, storage, access, and disposal standards
|
Establishes enterprise-wide rules for document management, record retention, and ethical information use
|
|
Impact
|
Drives operational efficiency and data-driven decision-making
|
Aligns information use with strategic objectives and regulatory obligations
|
|
Examples of Implementation
|
Centralized data catalog, defined data quality metrics, and clear ownership structures
|
Legal defensibility for deleted records, enterprise retention schedules, and communication governance policies
|
What is a workflow in n8n?
N8n defines it as: “a collection of nodes that automate a process. Workflows begin execution when a trigger condition occurs and execute sequentially to achieve complex tasks.”
What is an n8n AI Agent?
An AI agent is an application that can carry out tasks autonomously. That’s the core of it.
They do this by observing their environment (like incoming emails or form submissions), reasoning through what to do next, and taking action using tools they’ve been granted access to.
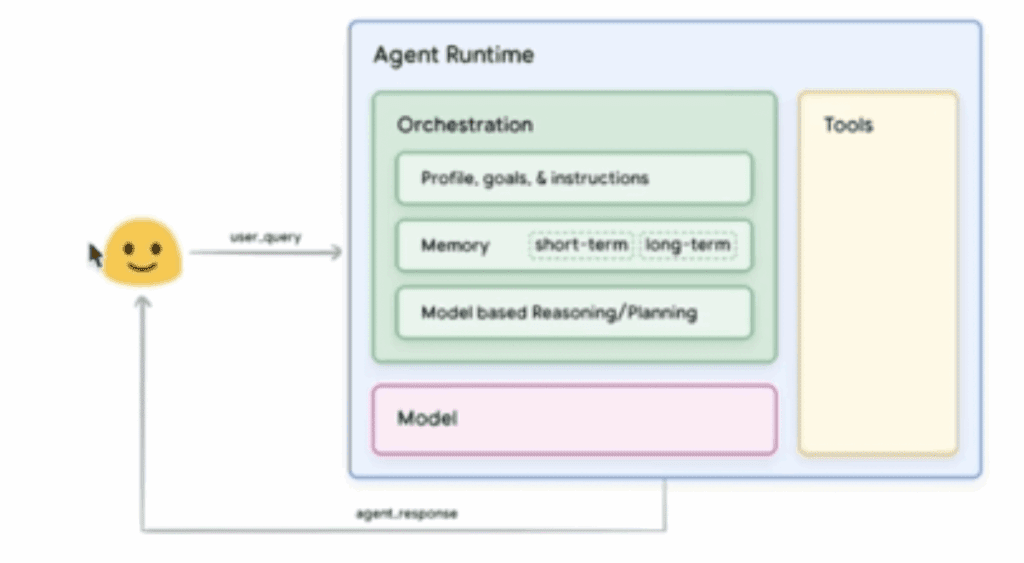
Every agent is made up of three layers:
- A model (the LLM): this is the agent’s reasoning engine, responsible for understanding, responding, and adapting. We like to think of it as the brain of your agent.
- An orchestration layer: this that handles memory, logic, branching decisions, and flow control.
- Tool access: what allows the agent to take action like sending emails, querying APIs, updating records, and more.
In the context of n8n, an AI agent is this entire system assembled into a visual workflow.
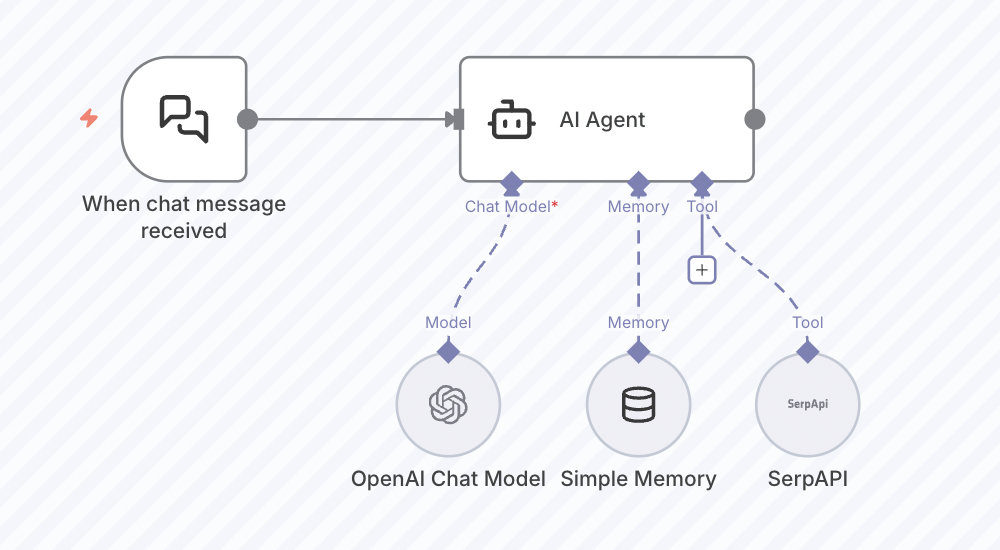
n8n itself is an open-source, low-code automation platform designed to help you stitch these systems together. Think of it as the scaffolding your agent operates within. It lets you define when to trigger actions, what the agent should do, and how it should behave over time. And you don’t need to write a single line of complex backend code. Anyone can do it.
You’re also not locked into pre-baked behaviors. You can wire in whatever models, tools, or prompts you need to make the agent behave exactly the way your use case demands.
For example, you could:
- Receive input from something like an email, webhook, or CRM
- Use a model like GPT-4 or Claude to interpret that input
- Make branching decisions based on logic or confidence
- Take real-world actions like respond to a message, update a record, push content, or route information
This could look like a support agent triaging incoming messages, a content assistant drafting posts from a single idea, or a data agent parsing and summarizing documents on a schedule.
Want to get deeper into what n8n can do? We’ve broken that down here in our complete guide to n8n.
What Makes the n8n AI Agent Different From Chatbots?
Most people’s exposure to AI is through a text box that generates a response when you ask a question. AKA a chatbot like ChatGPT.
But agents do more than answer. They take action.
Through n8n, you can build workflows where AI takes meaningful action across tools while following your own logic. That level of control matters. Because businesses like yours are looking for ways to operationalize AI inside their existing systems. They want:
- Transparent logic they can inspect and adjust
- Tool integrations they can configure
- Behavior they can test, tune, and monitor
n8n provides exactly that. It’s open-source, extensible, and fully customizable. You’re not locked into fixed templates, black-box flows, or “AI Lite” wrappers.
Compare that to platforms like Zapier, where flows are linear, limited, and expensive to scale with AI calls. Or Make, which offers more visual control but lacks the transparency and flexibility needed for real agent orchestration. n8n becomes the perfect AI companion.
See how those tools compare in greater depth: n8n vs Zapier and n8n vs Make.
Why Most Artificial Intelligence Agent Tutorials Fail to Scale
It’s easy to get a basic agent working. Where you input a message and get a reply. But the gap between that and a reliable, production-grade agent is wide, and most tutorials never cross it.
They usually skip over critical mechanics like:
- Memory and context handling (so the agent doesn’t forget what just happened)
- Decision points and edge-case logic (to route different outcomes the right way)
- Content workflows (turning AI output into usable formats or next steps)
- Feedback loops (capturing results to refine future behavior)
- Data persistence (saving state across workflows or user sessions)
Without these, agents break down fast. They repeat themselves, misinterpret context, fail silently, or deliver outputs that can’t be acted on.
In our walkthrough, we’ll touch on the foundational pieces, like short-term memory, conditional logic, and output formatting, while showing you how to structure workflows that can evolve toward more intelligent behavior over time.
If you want agents that actually do something and keep getting better, these are the pieces to start thinking about early.
What You Need to Know Before Building Your First n8n AI Agent
You don’t need to be a developer to build AI agents in n8n, but a solid grasp of the fundamentals will help you move faster and make smarter design choices.
Below are the key ideas and mechanics that shape how agents work in n8n, followed by some key concepts that will make your agents more capable and scalable.
How Agents Work in n8n
Triggers: Triggers are what start your agent’s workflow. This could be an incoming email, a webhook request, a form submission, or a scheduled check-in. You define what event should kick off the process.
Nodes: Nodes are the individual steps in your workflow. Each node performs a function like calling an API, processing data, generating a response, or storing information. You’ll connect these together to build out your agent’s logic.
Logic Control: With IF nodes, switches, and custom functions, you can introduce dynamic behavior like routing responses based on input type, confidence levels, or external factors.
Credentials: n8n stores API keys and logins as reusable credentials, letting you securely connect your agent to tools like OpenAI, Claude, Gmail, Airtable, or any REST API.
Execution Context: Every time your n8n workflow automation runs, n8n tracks its full execution, making it easy to reference earlier steps, reuse variables, and debug when things go wrong.
AI Agent Concepts That Make a Difference
Prompt Engineering + Context Passing
Your agent is only as good as the instructions you give it. That starts with a well-structured system prompt that clearly defines the agent’s role, task, tone, and constraints.
But it doesn’t stop there. As workflows get more complex, you’ll want to chain prompts across nodes, inject variables dynamically, and carry context from one step to the next. This allows the agent to adapt based on prior inputs, actions, or outcomes.
In n8n, that might mean:
- Using {{$json[“field”]}} references to pass user data between nodes
- Dynamically inserting instructions or parameters from previous steps
- Splitting logic into multiple LLM calls for better control and traceability
Memory & Long-Term Data
For multi-step agents or ongoing interactions, memory is essential.
n8n offers quick options like window buffer memory, which lets your agent retain the last few messages for short-term context. But for real persistence, you’ll want to store data externally. Such as in a database, Airtable, Redis, or another system.
This gives your agent the ability to:
- Remember prior conversations or actions
- Personalize behavior for different users
- Avoid repeating steps or instructions
If you’re not ready for full memory yet, start with structured outputs that can be stored and revisited later.
Agent Evaluation & Feedback Loops
Once your agent is doing something useful, the next step is making it better.
That starts with visibility: logging outputs, tracking behavior, and flagging when something doesn’t go as expected. From there, you can build simple feedback loops:
- Store outputs and responses in Airtable or Sheets for review
- Score responses manually (or with another agent)
- Feed corrected outputs back into the system for future prompts
This doesn’t need to be complex. Even a basic “was this helpful?” toggle or output log can make a huge difference in refining how your agent performs over time.
Building Your First n8n AI Agent: Step by Step
In the steps below, we’ll walk through a specific example of an agent that can send emails via Gmail. But the structure applies to almost any agent you want to build, and we’ll explain how you can swap in your own tools, prompts, and actions.
You’ll see screenshots from our internal build as we go. If you prefer to watch it in action, check out this TikTok walkthrough from our CMO Matt Paige.
Step 1: Add an AI Agent to Your Canvas
To create AI agents in n8n, you’ll need to start by opening a new workflow.

From there:
- Click “Add first step.”
- In the search bar that pops up, type “AI Agent.”
- Select the AI Agent node and drop it into your canvas.

Step 2: Add a Chat Model (LLM)
Now it’s time to give your agent a brain. This is the large language model (LLM) that will interpret input, generate responses, and drive decision-making.
- Click into the AI Agent node.
- Find the Chat Model field and choose your provider. n8n supports several:
- OpenAI (e.g., GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo)
- Anthropic Claude
- Mistral
- Or any model with an accessible API
- If this is your first time using a model, you’ll need to add credentials:
- Go to the Credentials section in n8n.
- Choose your provider and securely store your API key or token.
- Back in your agent node, select the specific model variant you want to use.
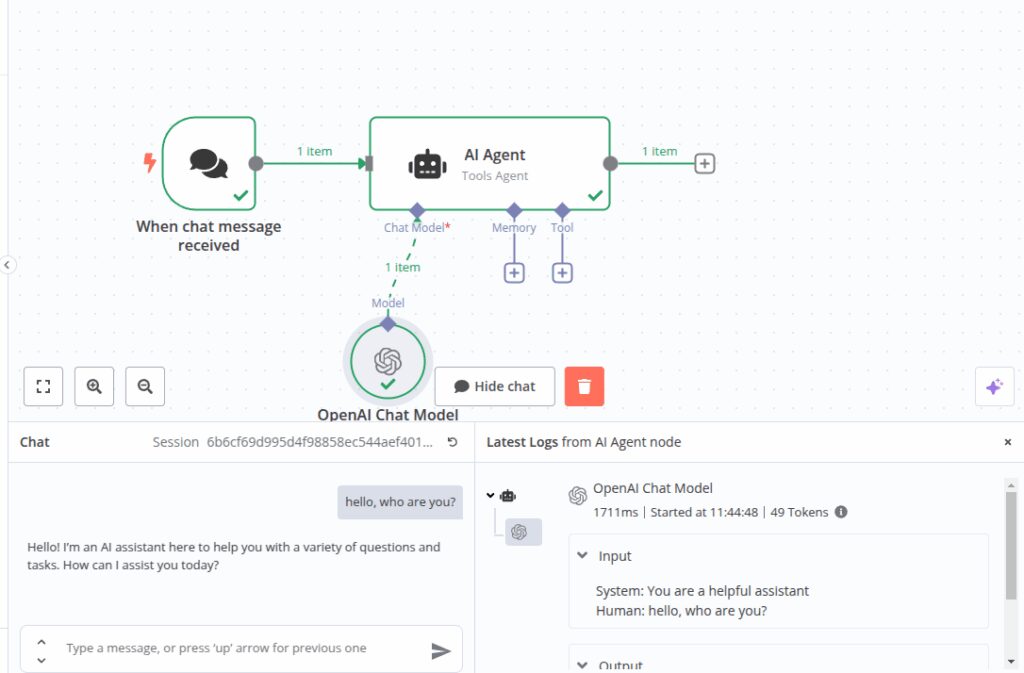
In our example, we used OpenAI’s GPT-4o. It’s a reliable, high-context model that works well for classification, response generation, and nuanced reasoning.
Your agent now has a mind of its own and can start making sense of incoming inputs.
To test it, open the chat function and ask, “Who are you?”
Step 3: Add Memory
Memory is what allows your agent to carry context across steps. Without it, every interaction starts from scratch.
For example, I asked my AI agent what my name was. Despite the fact that I introduced myself in the previous message, it claimed not to know my name or to have access to personal information about me.
To bring your simple agent to its full potential, you will need to add another node.
Inside the AI Agent node, scroll down to the Memory section. You’ll see a few options:
- Window Buffer: Stores the most recent interactions (like a chat message transcript). Ideal for short-term, single-session workflows.
- Data Store: Persists information across multiple runs. Useful for recurring agents or user-specific workflows.
- Custom: For advanced setups, like integrating with a database or external memory API.
In our example, we used Window Buffer to help the agent retain recent messages while classifying emails. It’s simple to set up and perfect for lightweight context tracking.

If your agent will be handling repeat users, doing multi-turn tasks, or referencing past interactions, plan for a more persistent memory layer (like Redis or Airtable).
Step 4: Connect a Tool
Now that your agent can think and remember, it’s time to make it useful by connecting it to a real-world tool. You can link your agent to almost anything: email clients, CRMs, databases, ticketing platforms, or internal APIs. In our example, we connected Gmail.

Here’s how that works:
- Drag a new node onto the canvas and choose your tool. In this case, Gmail.
- Choose an action:
- Read emails: Fetch unread messages from a specific label or inbox.
- Send emails: Automatically generate replies using the agent’s response.
- Extract fields: Like subject, sender, and message body.
Other popular options:
- Slack (send or route messages)
- Airtable (store classifications or feedback)
- HTTP Request (connect to any API)
This is where the agent stops being theoretical and starts taking action. The more powerful tools you connect, the more value your agent can deliver.
Whatever tool you’re using will need to be connected and authenticated to n8n. If you haven’t done that already, it’s pretty simple, you just need to: add credentials for that app in n8n, then select them in your node.
Step 5: Define the Output Format
Once your agent generates a response, you need to structure it for whatever tool it connects to next, whether that’s email, a database, Slack, or an API.
Add a Markdown or Text node after the Chat Model. Use it to format your response clearly. You can include:
- Summaries or responses
- Tags or classifications
- Structured formats like JSON, CSV, or form-ready fields
Formatting matters, especially when your agent is part of a larger system. A little structure goes a long way toward making outputs usable downstream.

Step 6: Craft Your System Prompt
Your system prompt defines the agent’s personality, tone, role, and task. So it’s worth taking a few extra minutes to get this right.
Inside the AI Agent node, find the System Prompt field.
This is where you’ll give your agent instructions like:
“You are a smart support agent. Classify incoming messages by topic and urgency. Respond in a friendly, professional tone. Tag each message with a category and response priority.”
You can write this yourself. Or, you can ask ChatGPT to help. Give it your use case and let it generate a prompt in Markdown format. This works especially well if you’re targeting specific output types, tones, or tools.
In our example, we used ChatGPT to generate a system prompt for an agent that sends emails on our behalf.

Step 7: Tell the Agent What to Do
Now it’s time to connect the input. This is what will trigger your agent and provide the raw user message.
- Add a trigger node to your canvas. Common options:
- Webhook: For receiving messages from an external app or website
- Email: For agents that handle incoming mail
- Schedule: For agents that run on a timed basis (e.g., daily summary generator)
- Link your trigger to the AI Agent node. The incoming data, often called the user query, will be passed into your model as input.
- From here, chain together any additional logic:
- Route based on classification
- Store the message or response
- Trigger a follow-up action via another API
This is the moment your agent comes to life. It receives a real input, reasons through your system prompt, and takes action based on how you’ve structured the logic.
Step 8: Check That It Works
Now for the payoff. Click Execute Workflow in n8n and let your agent run.
You’ll see each node light up as it executes. All green means success. If something fails, you’ll get a red node and a detailed log of what went wrong.
But you still want to run your own checkpoints:
- Is the user message reaching the model?
- Is the output formatted the way you expect?
- Did the tool (like Gmail) take the correct action?
If something’s off, tweak your system prompt, logic, or formatting node. Don’t be afraid to iterate. Even simple agents can take a few tries to fine-tune.
And that’s it. You’ve built your first working AI agent.
You may also like: AI Agent Design Best Practices You Can Use Today
How to Add Conditional Logic to Your Agent
Not every user asks the same question. Not every API responds the same way. And not every workflow should follow a single path.
To account for that, we use conditional logic. Conditional logic gives your agent the ability to sense, evaluate, and decide in real time.
Here’s how to bring that adaptability into your build:
Using IF/ELSE Nodes
The IF and Switch nodes in n8n let you evaluate conditions and split the workflow based on the results. This means your agent can:
- Route based on classification results from your LLM
- Change behavior depending on user input (e.g., “urgent” vs. “general”)
- Handle different scenarios without rewriting your whole flow
It’s a simple way to turn linear logic into something responsive.
Handling Tool Failures Gracefully
Real-world tools fail all the time. Maybe your email API hits a rate limit, your LLM times out, or the input is malformed.
Conditional logic lets you catch and respond to those failures, without breaking complex workflows.
You can:
- Add retry logic with a delay node
- Send fallback messages (“We’re working on it, please try again.”)
- Trigger alerts to your team when something breaks repeatedly
Even basic error handling makes your agent significantly more reliable and more trustworthy for product managers or teams depending on it.
Orchestrating Multiple Tools with One AI Agent
Real AI workflows often span multiple tools.
Let’s say you want your agent to:
- Read a new email (Gmail)
- Analyze the message (LLM)
- Classify it (Prompt + logic)
- Post a summary to Slack
- Store the output in Airtable for tracking
Each of these actions happens in sequence, where you’re routing data through a chain of services to solve a business problem.
To build this in n8n:
- Start with your trigger — usually a webhook or email
- Add an AI Agent node for your reasoning layer
- Connect downstream tools (e.g., Slack, Airtable) as separate nodes
- Use Set, Merge, or IF nodes to shape and route data between steps
The more tools your agent can coordinate, the closer you get to unlocking its full potential.
From Tutorial to Production: Scaling n8n AI Agents
Once your agent is working locally, the next step is production-readiness. That means making sure it runs reliably, scales with usage, and can be monitored and improved over time.
Here’s what to consider:
1. Move to a Cloud-Based n8n Instance
Local builds are great for testing, but production agents need to run continuously and be accessible by your systems or users. You can:
- Self-host n8n using Docker or a VM
- Use n8n’s cloud platform (with usage-based pricing
- Deploy to services like AWS, Azure, or Railway
Make sure your deployment includes environment variables and credentials management to keep things secure.
2. Monitor Uptime and Handle Rate Limits
Agents can fail silently if you’re not watching.
Use built-in n8n monitoring (or external tools like Sentry or Grafana) to:
- Track execution counts
- Catch errors or tool failures
- Watch for rate limits, especially on LLMs or APIs
Add retry logic where needed, and consider introducing delay nodes to manage high-throughput workloads.
3. Persist Outputs for Analytics and Training
Storing the results of each run helps with performance tracking and continuous improvement.
You might:
- Log responses to Airtable, Postgres, or BigQuery
- Tag each run with metadata (user, use case, result)
- Use this data to tune prompts, evaluate effectiveness, or train custom models later
If your agent needs long-term memory or session awareness, connect it to a data store like Redis, a database, or n8n’s built-in Data Store node.
Real-World Use Cases of n8n AI Agents
Once you understand how to build an agent, it’s time to think about what it can actually do. These two public workflows show how teams are using n8n to build AI agents that solve real business problems. Take them as inspiration to make your own work and life easier.
Content Creation at Scale
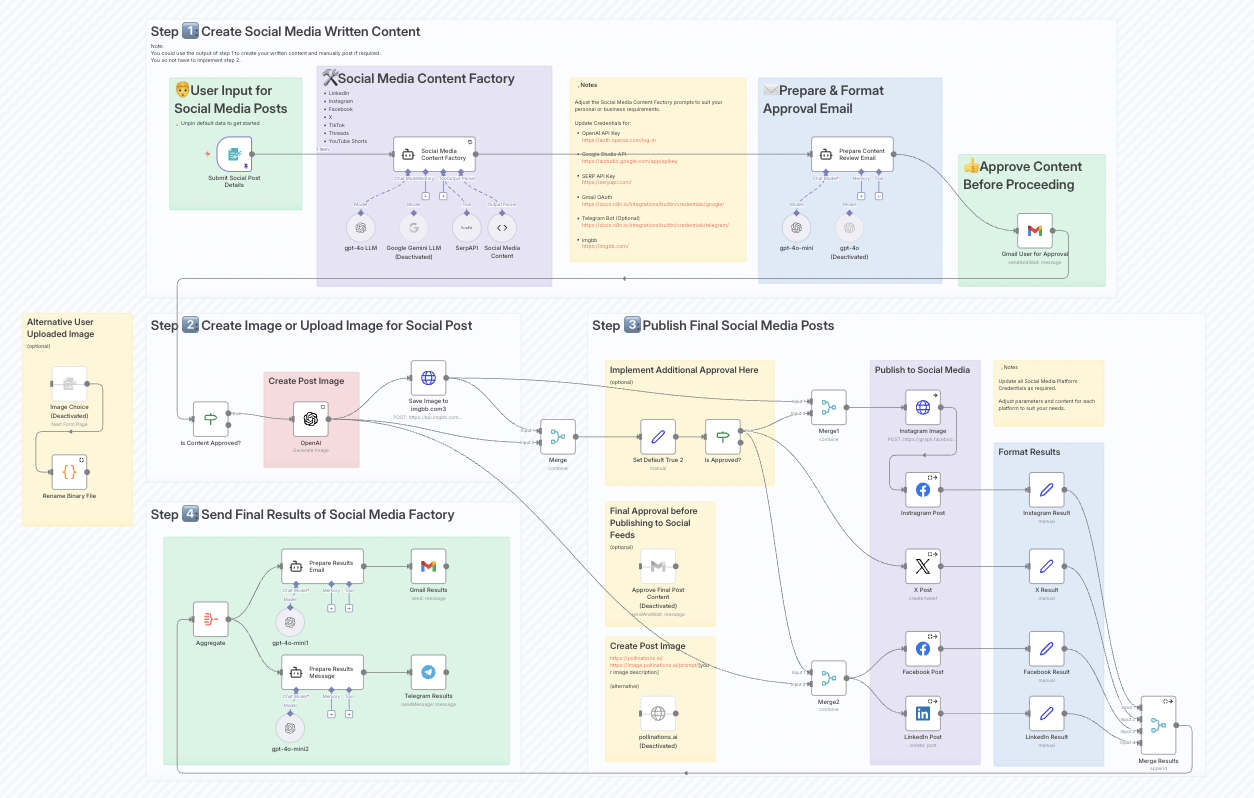
Joseph LePage, an n8n community contributor, created a public workflow that automates content generation for seven platforms, including LinkedIn, Twitter, TikTok, and YouTube Shorts.
The workflow starts with a single prompt submitted via form or webhook. From there, an LLM generates post variants tailored to each platform. The workflow formats the output using Markdown nodes and routes each version to the right publishing queue or CMS.
The result is more consistent publishing and less manual lift for marketers, all from a low-code canvas.
AI-Powered Customer Support

Resources to Help You On Your Way
If you’re ready to go deeper with AI agents in n8n, here are some curated resources to build your skills and accelerate your next build:
Official Docs & Templates
- n8n Documentation – everything from node setup to credential management
- n8n Workflow Templates – explore and clone existing AI agent builds
Courses & Tutorials
- Udemy: AI Agents with n8n – learn to build AI content agents step by step
- GitHub: Search for n8n + AI agent examples to learn from community projects
You may also benefit from n8n’s two-part video series for building agents:
- Part 1: Building AI Agents: Chat Trigger, Memory, and System/User Messages Explained
- Part 2: Building AI Agents: AI App Tools and Guardrails explained, Gmail Draft Agent
Hatchworks AI Blog
We talk AI, agents, and Generative-Driven Development all the time on our blog and our podcast. Here are a few links to get you started:
Experiment with HatchWorks AI
Want to see what’s possible when you combine AI agents with real business workflows? Join our AI Agent Opportunity Lab.
It’s an innovation space for hands-on prototyping, where you can:
- Test AI workflows tailored to your org
- Collaborate with our team of product, data, and automation experts
- Explore use cases before you commit to full-scale development
Whether you’re new to exploring automation or a tech lead evaluating agentic systems, the Lab is where ideas get built, fast.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI Agents in n8n
What’s the difference between AI and automation in n8n?
Automation in n8n refers to workflows triggered by specific events, like receiving a webhook, sending an email, or updating a CRM.
AI introduces reasoning. It lets workflows interpret, classify, and generate responses based on natural language. When you combine both, you move from fixed actions to intelligent, adaptive workflows that respond to user input with more nuance.
Can I fine-tune responses?
While you can’t fine-tune base models like GPT-4 directly inside n8n, you can tailor behavior with well-structured prompts, memory, and logic layers. You can also feed the model “knowledge” using previous messages, context variables, or external sources. This gives the illusion of training without modifying the model itself.
Is it secure for enterprise use?
Yes, especially when hosted on your infrastructure or through vetted cloud providers. You control credentials, environment variables, access levels, and even whether workflows connect to the open internet.
For teams working in regulated environments or with sensitive systems (like internal tools or MCP servers), n8n offers the visibility and control many closed platforms can’t.
If you’re looking for all the details on how to deploy securely, the n8n documentation has step-by-step guidance, or you can reach out to our team at HatchWorks AI for further support on your builds.



