The tech sector is still grappling with a critical and complex challenge: the rising shortage of software developers. It’s been simmering for years but has reached a critical point, affecting businesses and technological progress on a global scale.
Tech talent shortage statistics reveal a projected shortage of technology professionals in the US across various industries, emphasizing the depth of the digitization-driven skills crisis within America’s STEM workforce. This highlights the severity of the shortage with factual data, underscoring the urgent need for solutions.
But a transformative wave is sweeping through – the Generative AI Revolution.
A new emerging paradigm, fueled by AI-powered software development and AI-enhanced software engineers, is not just about technological advancement but a beacon of hope in finally addressing the developer shortage.
The increasing reliance on digital solutions across industries has led to soaring demand for highly skilled software developers everywhere, a demand that the current workforce pipeline is struggling to satisfy.
This gap between supply and demand is causing significant disruptions, from delayed project deliveries to inflated development costs, impacting sectors far beyond the traditional tech industry.
In this blog, we explore the software developer shortage, its causes, and how it affects businesses. We’ll also look at how generative AI and other AI-powered tools could help solve this problem.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
Understanding the Shortage of Software Developers
In 2024, the software developer talent shortage has become more pronounced than ever. Understanding the magnitude of this issue is crucial for businesses, educational institutions, and policymakers as they strategize to bridge this growing gap in the tech workforce.
The tech talent shortage is expected to reach 85.2 million by 2030, further emphasizing the global scale of this issue. Delving into tech talent shortage statistics reveals a projected shortage of technology professionals in the US across various industries, highlighting a digitization-driven skills crisis within America’s STEM workforce.
This analysis underscores the depth of the skills crisis, with specific sectors like artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain technology, and cybersecurity facing the most acute shortages.

Today, over half of jobs require technology skills, and this number is expected to grow to more than 77% in less than a decade, highlighting the increasing necessity of tech proficiency in the job market.
The United States alone currently boasts over 1.6 million developers, software engineers, quality assurance analysts, and testers, a number expected to surge by 25% to over 2 million by 2031, much faster than the average growth rate for all occupations.
This growth underscores the escalating demand for highly skilled software engineers and developers, particularly in specialized areas such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain technology, and cybersecurity, where the scarcity of professionals with the necessary qualifications and skills is most acute.
This shortage is not uniformly distributed across the globe. Certain regions, particularly those with rapidly growing tech industries, face more acute shortages.
In contrast, other areas with robust educational systems in technology seem to be fairing slightly better, though they are not immune to the challenge.
This geographical disparity suggests that the issue is intertwined with factors like educational infrastructure, local industry demands, and regional economic conditions.
Further complicating the scenario, a Gartner report highlights that fifty percent of technologies where talent availability is the top risk factor were rated as high-risk.
Additionally, a survey by Infragistics points out that more than a third of respondents (37.5%) anticipate continued difficulties in recruiting skilled developers, especially in specialized roles such as DevOps Engineers, Data Analytics Developers, and IT Security Engineers.
 Hiring managers, in particular, are struggling to find professionals with these qualifications and skills, attributing the talent shortage to the increasing complexity of the industry and the rising popularity of these technologies across various sectors.
Hiring managers, in particular, are struggling to find professionals with these qualifications and skills, attributing the talent shortage to the increasing complexity of the industry and the rising popularity of these technologies across various sectors.
These stats not only underscore the extent of the problem but also set the stage for a deeper exploration into the causes and ramifications of this global shortage.
Challenges in Project Delivery Due to the Shortage
The shortage of software developers in 2024 is having a pronounced impact on project delivery across various industries. One of the most immediate consequences is the delay in project timelines.
With fewer skilled developers available, companies are struggling to keep up with their development schedules. This is not just about delayed product launches; it’s about the cascading effect these delays have on overall business strategies and market competitiveness.
For instance, a tech company might miss a crucial window for launching a new app or software update, allowing competitors to capture market share.
Quality is another casualty in this scenario. Understaffed development teams, often working under tight deadlines, are prone to releasing products with bugs or subpar features, impacting customer satisfaction and trust.
A case in point is a recent incident involving a major financial services firm, which had to recall a software update due to performance issues, causing not just financial loss but also reputational damage.
Internally, the strain on existing staff cannot be overstated. Overburdened with work, talented developers may experience burnout, leading to decreased productivity and even attrition, further exacerbating the shortage problem.
Cost Implications
Financially, the software developer shortage is a double-edged sword for businesses. On one hand, companies are increasing salaries and offering more substantial benefits to both attract software talent and retain talent.
This trend is inflating the overall cost of maintaining an in-house development team, impacting the bottom line of businesses, especially startups and small enterprises. On the other hand, many companies are turning to outsourcing and hiring freelance developers as alternative solutions.
While this approach can provide access to a broader technical talent pool, it comes with its own set of challenges and costs. Managing remote teams, ensuring quality, and integrating external work into existing projects can add complexity and expense without the right partner.
These financial pressures are particularly acute for smaller businesses, which may find it challenging to compete with larger corporations in terms of salaries and benefits. The result is a competitive imbalance, where smaller players struggle to keep pace with their more resource-rich counterparts in the tech development race.
5 Reasons Behind the Shortage of Software Engineers
1. Rapid Technological Advancements: Central to this issue is the rapid pace of technological advancement, which has significantly outstripped the current educational and training frameworks. The evolution of fields like AI, blockchain, and advanced data analytics has created a demand for skills that current educational curricula are struggling to address quickly enough.
2. Inadequate Educational and Training Frameworks:
Despite the availability of online resources, short courses, and certifications, there is a significant delay in integrating these new technological needs into mainstream education systems.
This has led to a substantial skills gap, where the demand for advanced technical competencies and skilled tech workers far exceeds the supply.
Investing in upskilling aspiring software developers through access to online educational resources, short courses, and certifications in computer science basics and programming languages is crucial. This approach not only addresses the immediate skills gap but also prepares these individuals for the evolving demands of the tech industry.
3. Growing Industry Demand:
According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, the job growth rate for software developers, QA analysts, and testers is expected to grow by 25% from 2022 to 2032, much faster than the average for all occupations.
This underscores the pressing need for more tech professionals as nearly 200,000 developer positions will need to be filled annually by 2030 in the U.S. alone.
4. Global Economic and Employment Trends:
Another critical factor is the digital transformation that is sweeping across various industries. With more businesses integrating digital solutions into their operations, the need for software developers has skyrocketed.
This demand is not limited to the technology sector but extends to healthcare, finance, retail, and more, compounding the shortage.
Recent studies indicate that 47% of technologists have had to take on more tasks due to the talent shortfall, and almost 50% of recruiters struggle to find qualified candidates for job openings. These statistics reflect the acute pressure on current professionals and the difficulties faced by employers to find talent in the tech industry.
5. Demographic and Career Preference Changes:
Further complicating the scenario, demographic changes and shifts in career preferences also play a significant role. The aging workforce in certain regions, coupled with a diminishing interest in software engineering careers among younger generations in other areas, exacerbates the problem.
Additionally, global economic trends, including the rise of start-ups and the gig economy, have redistributed the available technical skills and talent further, challenging traditional hiring models.
These factors collectively contribute to the current state of the software developer shortage. It’s a problem rooted in both the rapidly evolving landscape of technology and the changing dynamics of the global workforce.
How to Solve the Shortage
The Generative AI Solution to the Developer Shortage
The advent of generative AI is ushering in a new era in software development, one that holds promise in addressing the chronic shortage of software developers.
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence that can generate code, automate testing, and even debug programs, thereby enhancing the efficiency of the development process.
 Tools like OpenAI’s Codex and GitHub’s Copilot are prime examples, offering automated code suggestions and helping developers write code faster and with fewer errors.
Tools like OpenAI’s Codex and GitHub’s Copilot are prime examples, offering automated code suggestions and helping developers write code faster and with fewer errors.
This technology is not just about speeding up development; it’s also about making development more accessible. By automating routine aspects of coding, generative AI allows developers to focus on more complex and creative tasks.
This shift can lead to a reduction in the overall workload and help mitigate the impact of the developer shortage.
Successful case studies, such as AI-assisted development projects in fintech and healthcare, illustrate the potential of generative AI. In these cases, AI tools have not only accelerated development timelines but also enhanced the overall quality of the software products.
Limitations and Concerns
However, the reliance on generative AI comes with its own set of limitations and concerns. One significant limitation is the complexity of tasks that AI can handle.
While AI is excellent at automating routine coding tasks, it still requires human oversight, especially for complex, creative, or nuanced development work.
 Quality and security are also major concerns. The code generated by AI needs to be thoroughly reviewed and tested, as it can introduce unique bugs or vulnerabilities not typically found in human-written code.
Quality and security are also major concerns. The code generated by AI needs to be thoroughly reviewed and tested, as it can introduce unique bugs or vulnerabilities not typically found in human-written code.
Ethical considerations are another crucial aspect. The potential for job displacement and the responsible use of AI tools in development raises important questions about the future of the workforce.
A balanced approach is essential, where AI is seen as a tool to augment human developers, enhancing their productivity and creativity, rather than replacing them.
Education and Training Initiatives
In response to the escalating software developer shortage, a significant shift is occurring in education and training. Educational institutions, in collaboration with the tech industry, are revamping their curricula to better reflect the rapidly changing technological landscape.
For example, several universities have introduced courses focused on emerging technologies like AI, cloud computing, and blockchain, aiming to produce graduates who are immediately ready to contribute to the tech sector and workforce.
Tech companies are not merely passive beneficiaries of this serious talent gap either; many top tech giants have taken an active role in nurturing future software developers. Initiatives such as scholarships, mentorship programs, and partnerships with coding boot camps have become increasingly common.
Moreover, there’s a growing emphasis on continuous learning and professional development. Companies are investing in training their existing workforce in new technologies and methodologies, acknowledging that skill enhancement is a continuous process in the ever-evolving tech landscape.
Utilizing Remote Workers and Staff Augmentation
Another strategy that businesses are adopting to combat the developer shortage is leveraging remote work and staff augmentation.
The rise of remote work has enabled companies to tap into a global tech talent pool, no longer limited by geographical constraints.
To effectively attract talent, it’s crucial for companies to consider broadening their search for technical talent globally as a strategy to mitigate the talent shortage.
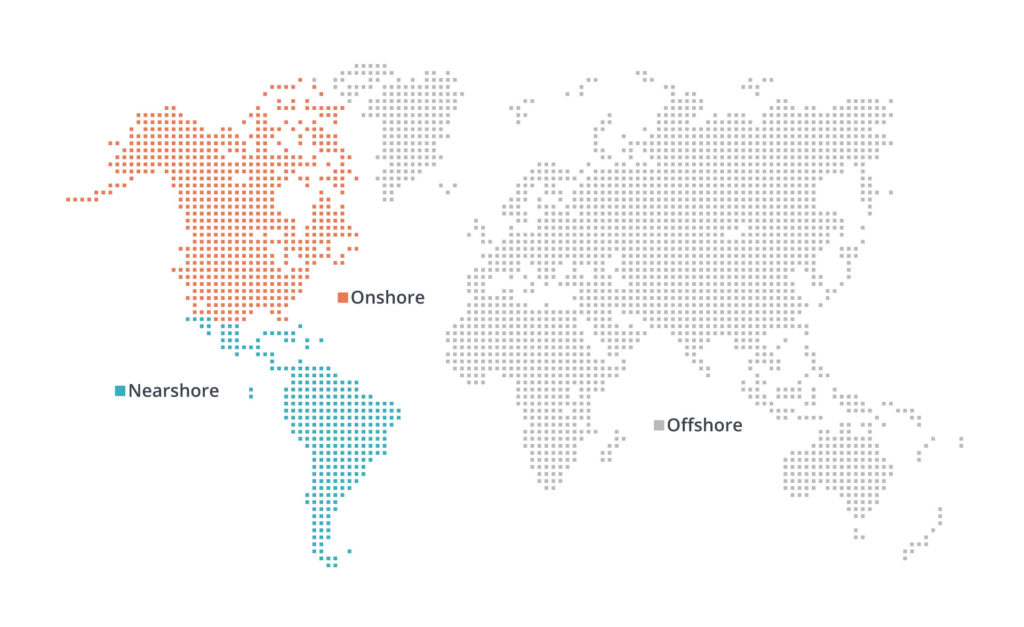
This approach not only broadens their search for skilled developers but also offers cost advantages and operational flexibility.
The gig economy is also playing a pivotal role in using software talent in this context. Freelance software developers are increasingly sought after, offering expertise on a project basis. This trend reflects a shift in the workforce dynamic, with many developers preferring the flexibility of freelance work.
However, this approach comes with its own set of challenges. Ensuring effective communication, maintaining a consistent quality of work, and integrating external contributors into internal teams are some of the hurdles companies face.
Despite these challenges, the move towards remote work and staff augmentation is likely to continue, potentially becoming a standard practice in the industry and a key factor in addressing the software developer shortage.
Future Trends in Software Development
As we look toward the future, certain trends are emerging that will likely shape the industry. Experts predict a significant rise in the adoption of low-code/no-code platforms and Generative AI, enabling individuals with minimal coding experience to create applications, thereby partially addressing the developer shortage.
Cybersecurity is also expected to become a more integral part of software development, as the frequency and sophistication of cyber threats, especially due to Gen AI, continue to rise. This trend will likely create new roles focused on security aspects.
Emerging technologies and artificial intelligence are also expected to redefine the skill sets required for software developers. Developers will need to be adaptable, continuously learning, and proficient in newer technologies. For those entering the computer science field, as well as for seasoned professionals, this means a constant evolution in terms of technical skills and knowledge.
Innovative Solutions on the Horizon
Looking ahead, several innovative solutions are poised to significantly alleviate the software developer shortage.
Among these, AI-driven development platforms like CoPilot offer developers a coding sidekick, enhancing their productivity and accuracy.
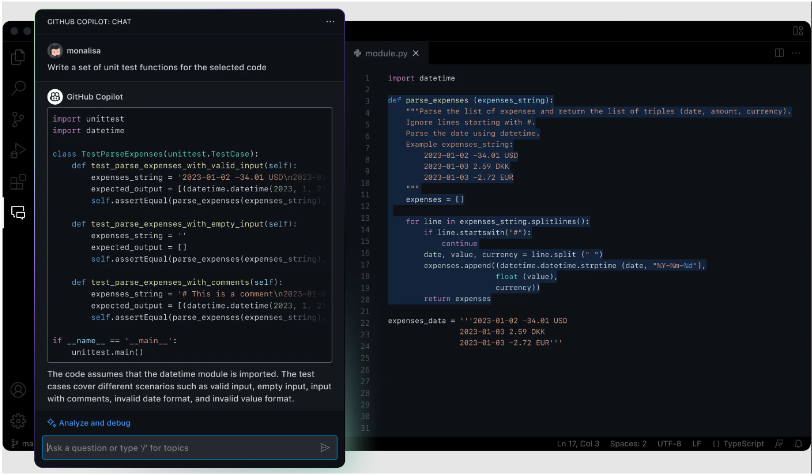
Additionally, AI orchestration and AI agents are becoming more prevalent, helping streamline complex tasks and decision-making processes.
According to Gartner, software development is the leading area for generative AI investment, with 55% of organizations already in piloting or production mode with these technologies.
McKinsey’s research further supports this trend, identifying software development as an industry ripe for productivity enhancement through Generative AI.
The Nielsen Norman Group has also found that the use of Generative AI tools can boost employee productivity by up to 66%, underscoring the transformative potential of these innovations [3].
At HatchWorks, we’ve integrated Generative AI into our development process, coining it Generative-Driven Development™.
This approach leverages cutting-edge AI to optimize various stages of software projects, from defining feature and UX flows to drafting concepts, prototypes, and even code generation.
Our experience shows a 30-50% increase in productivity for our clients, demonstrating the substantial benefits of AI integration.
Closing Thoughts
As we’ve explored the issue of the software developer shortage in 2024, it’s clear that the impact extends beyond individual organizations, influencing the global economy and the future of work. The integration of AI tools and platforms into software development is not just a temporary remedy but a transformative shift that promises to reshape the industry.
Continuing to engage in discussions about these advancements, exploring further innovations, and staying informed about the evolving landscape is essential. By embracing these technologies, the software development community can not only address the current skills shortage but also pave the way for a more efficient and productive future in technology.
We’re ready to support your project!
Instantly access the power of AI with our AI Engineering Teams.





